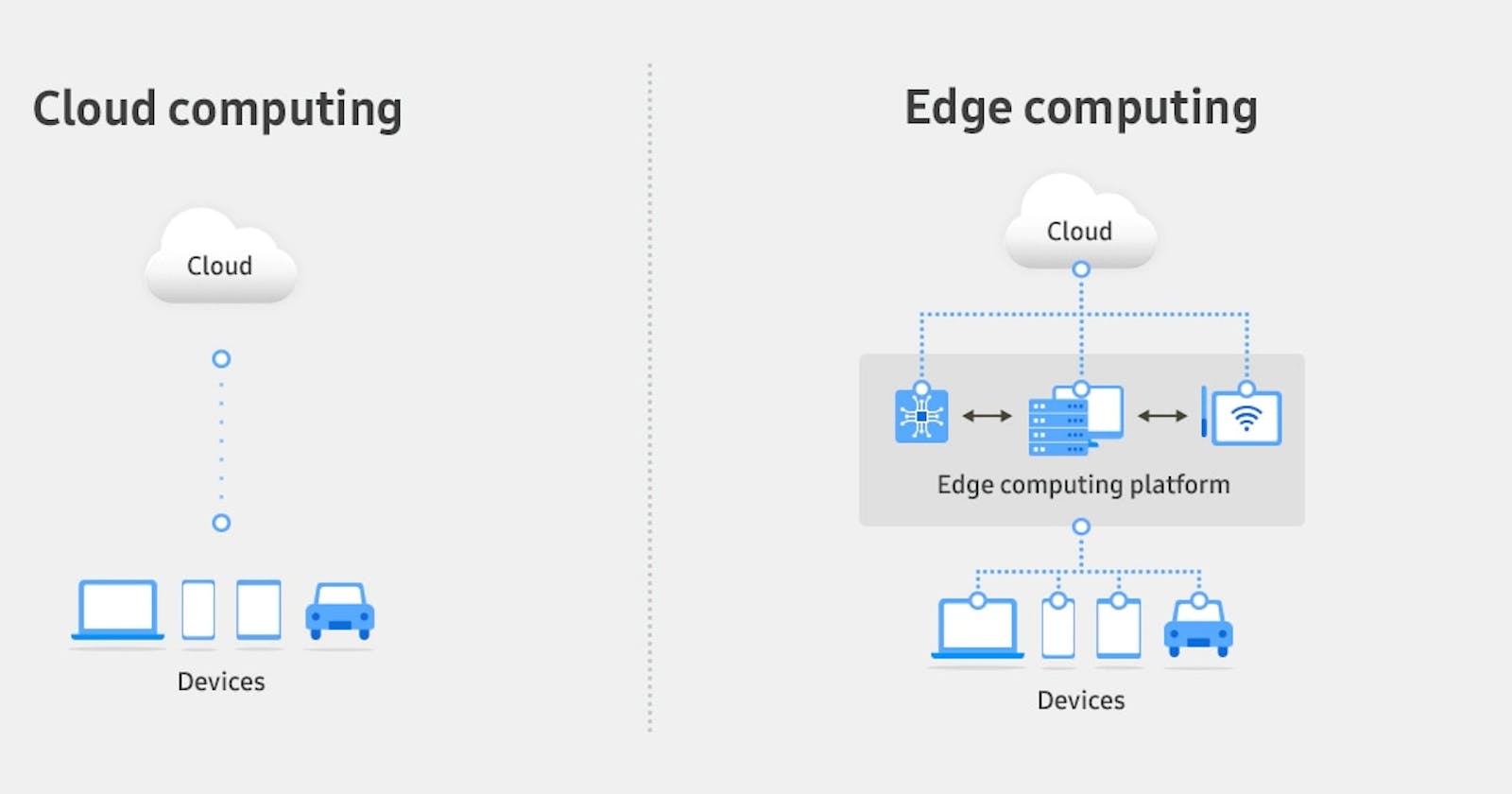
Edge computing and cloud computing are two paradigms in the realm of distributed computing, each with its own set of use cases, advantages, and disadvantages.
EDGE COMPUTING
Use Cases
Edge computing brings computation and data storage closer to the location where it is needed, reducing latency and bandwidth usage.
It's commonly used in scenarios where real-time data processing is crucial, such as IoT devices, autonomous vehicles, and industrial automation.
Edge computing is also valuable in situations where network connectivity is unreliable or limited, allowing local processing to continue uninterrupted.
Advantages
Reduced latency: By processing data closer to the source, edge computing minimizes the time it takes for data to travel to and from centralized servers.
Improved scalability: Distributing computation to edge devices allows for more scalable and efficient systems, especially in scenarios with a large number of devices.
Enhanced privacy and security: Data processing and storage at the edge can provide better privacy and security by minimizing the need to transmit sensitive information over networks.
Disadvantages
Limited resources: Edge devices typically have limited computational power and storage capacity compared to centralized cloud servers.
Management complexity: Managing a distributed network of edge devices can be complex and challenging, requiring robust infrastructure and monitoring tools.
Lack of standardization: The edge computing ecosystem is still evolving, leading to a lack of standardization across platforms and devices.
CLOUD COMPUTING
Use Cases
Cloud computing involves delivering computing services over the internet, providing access to a wide range of resources such as servers, storage, databases, and software.
It's commonly used for hosting websites and web applications, data storage and backup, development and testing environments, and running enterprise applications.
Cloud computing also enables on-demand access to computing resources, allowing businesses to scale up or down based on their needs without the upfront investment in hardware.
Advantages
Scalability: Cloud computing offers virtually unlimited scalability, allowing businesses to easily scale their resources up or down based on demand.
Cost-effectiveness: Pay-as-you-go pricing models allow businesses to pay only for the resources they use, reducing upfront costs and eliminating the need for investment in physical infrastructure.
Accessibility: Cloud services can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling remote work and collaboration.
Disadvantages
Security concerns: Storing sensitive data on third-party servers raises security and privacy concerns, especially in highly regulated industries.
Dependency on internet connectivity: Cloud services require a reliable internet connection, and downtime or network issues can disrupt operations.
Vendor lock-in: Migrating between different cloud providers can be challenging and costly, leading to vendor lock-in and limited flexibility.
CUDOS in Cloud Computing and Web3
CUDOS, being a cloud computing project, has contributed to the advancement of cloud services and Web3 in several ways:
CUDOS Intercloud: This is a network contributed by many distributed service providers, creating a diverse and international ecosystem. Currently, CUDOS compute supply spans 7+ countries, boasting over 12,000+ processor cores, 26,000GiB+ memory, 575TB+ storage, and an armada of GPUs in various models including the sophisticated NVIDIA A100s, A40s, V100s, H100s, and lot more. Whether it’s AI applications, media production, or web3 infrastructure nodes, the possibilities are as limitless as the stars with CUDOS InterCloud.
medium.com/cudos/cudos-intercloud-goes-live..
Scalability: CUDOS provides additional computational resources to cloud services, enabling them to scale more efficiently to meet growing demand.
Cost-effectiveness: By leveraging CUDOS' decentralized computing resources, cloud services can reduce their operational costs and offer more competitive pricing to users. Currently on the InterCloud, users can deploy a VM they can afford to pay for in various payment methods not limited to CUDOS tokens only.
Resilience: Integrating CUDOS into cloud infrastructure can enhance resilience by distributing computing tasks across a decentralized network, reducing the risk of downtime or service disruptions.
Decentralization: In the context of #Web3, CUDOS can support decentralized applications (dApps) by providing access to decentralized computing power, enabling the execution of smart contracts and other complex computations on distributed networks.
docs.cudos.org/docs/build/intro
In summary, while edge computing and cloud computing have different characteristics and use cases, both play important roles in modern computing ecosystems. CUDOS' integration with cloud services and its potential contributions to Web3 highlight the evolving landscape of distributed computing and the opportunities for innovation in this space.
To learn more about CUDOS, their InterCloud and all that they are building, visit 👇